OVERVIEW
The Seismic Load Analysis Procedure has 16 processes and it is largely divided into 2 parts : Series 1 (Including Series 2 , 3 & 4) and Series 5 (Modal Response Spectrum (RS) Analysis.
The part we will look over today is Series 5 : Modal Response Spectrum (RS) Analysis.
Modal Response Spectrum(RS) Analysis
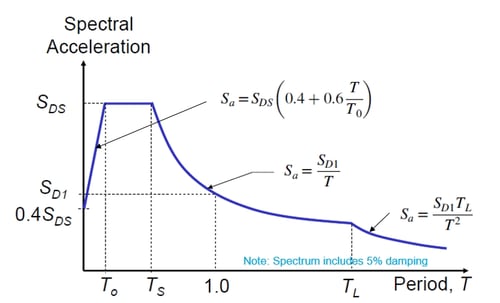
Where
⋅ SDS = the design spectral response acceleration parameter at short periods
⋅ SD1 = the design spectral response acceleration parameter at a 1-sec period
⋅ T = the fundamental period of the structure, sec
⋅ T0 = 0.2(SD1/SDS )
⋅ TL = long-period transition period(s) shown in Figs. 22-14 through 22-17
Basic Steps in RS Analysis
1. Compute modal properties for each mode
> Frequency (period), Shape, Modal participation factor, Effective modal mass
2. Determine number of modes to use in analysis
> Use a sufficient number of modes to capture at least 90% of total mass in each direction.
3. Compute spectral accelerations for each contributing mode
> Use a general spectrum.
4. Compute modified spectral accelerations
> Multiply spectral accelerations by modal participation factor and by (I/R).
5. Compute modal displacements for each mode
6. Compute element forces in each mode
7. Statistically combine modal displacements to determine system displacements
> SRSS or CQC
8. Statistically combine component forces to determine system displacements
> SRSS or CQC
9. Scale-up seismic load of RS
> If the design base shear based on modal analysis is less than 85% of the base shear(Equivalent Lateral force) computed using T=TaCu.
→ combination of modes must be scaled such that the base shear equals
0.85 times the equivalent lateral force.
10. Add accidental torsion
> As a static loading and amplify if necessary
11. Check story drift
> multiply the results of the modal analysis
(including the I/R scaling but not the 85% scaling) by Cd/I.
1. The Setting of RS Analysis in nGen
2. Add Signs(+, -) to the Results
3. Analytical Modeling for RS Analysis
4. Calculation of Base Shear by RS Analysis
1. The Setting of RS Analysis in nGen
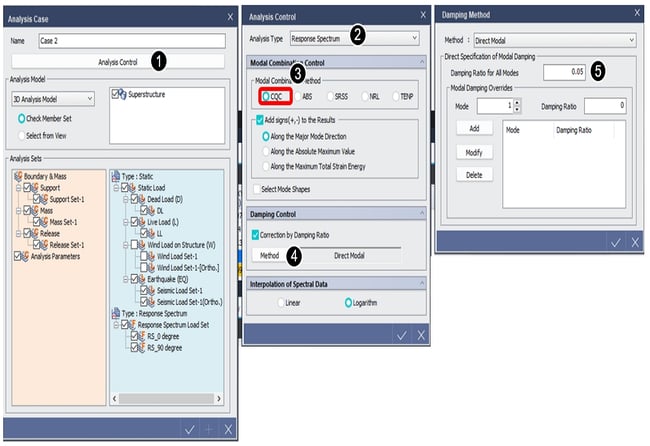 1. Click "Analysis Control" in "Analysis case" dialog box.
1. Click "Analysis Control" in "Analysis case" dialog box.
2. Select "Response Spectrum" in analysis type.
3. Select modal combination method. (use CQC generally).
4. Click "Method" button in damping control.
5. Modify damping ratio if necessary.
2. Add signs(+, -) to the Results
: Specify whether to restore the signs deleted during the mode combination and specify the restoration method.
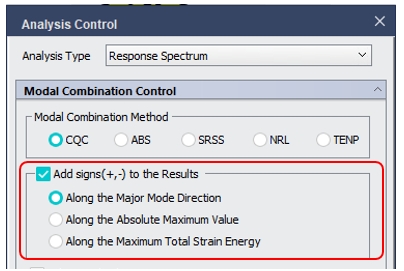
Along the Major Mode Direction: Restore the signs according to the signs(+, -) of the principal mode for every loading direction.
Along the Absolute Maximum Value: Restore the signs according to the signs of the absolute maximum values of the modal results.
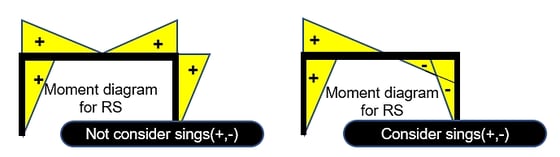
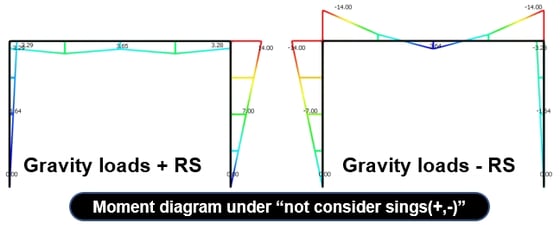
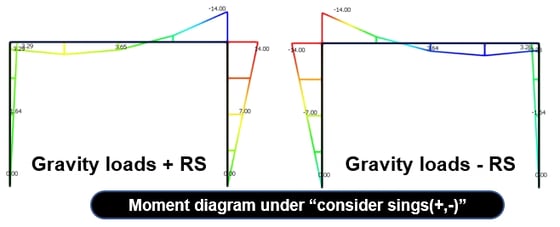 In both cases, the same design results can be obtained, but the sign(+,-) must be considered in order to find the actual member force.
In both cases, the same design results can be obtained, but the sign(+,-) must be considered in order to find the actual member force.
3. Analytical Modeling for RS Analysis
• Use 3D analysis
• For concrete structures, include the effect of cracking (consider a stiffness for cracked section).
• For steel structures, include panel zone deformations.
• Include flexibility of foundation if well enough defined
• Include actual flexibility of diaphragm if well enough defined
• Include P-delta effects in the analysis if the program has the capability
• Do not try to include accidental torsion by the movement of the center of mass
• Include orthogonal load effects by running the fill 100% spectrum in each direction, and then SRSSing the results.
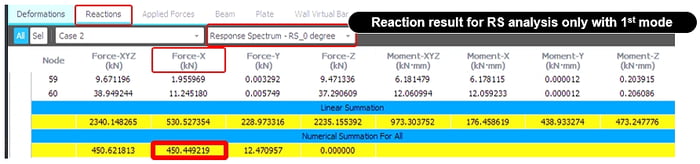
4. Calculation of Base Shear by RS Analysis
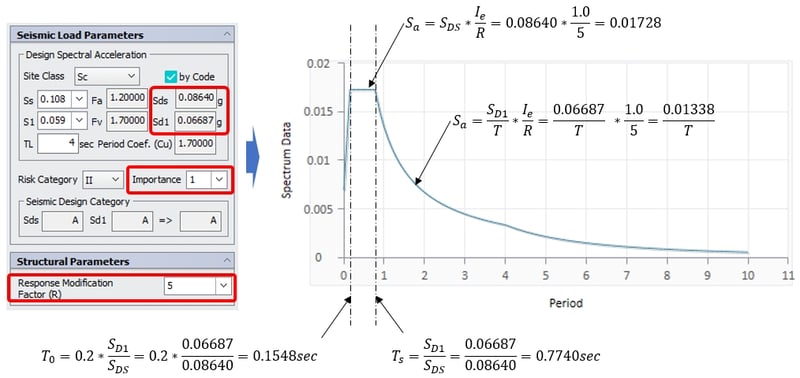
Generation of RS
Base shear(x-dir) for example model
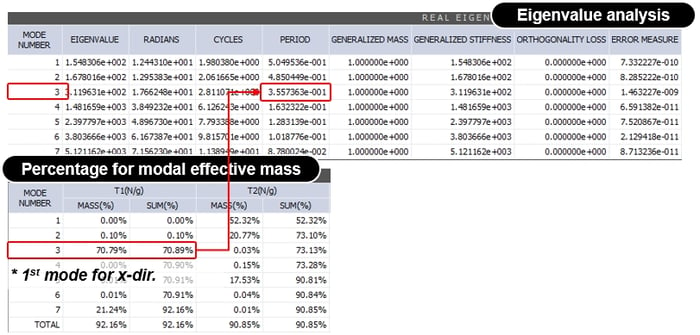
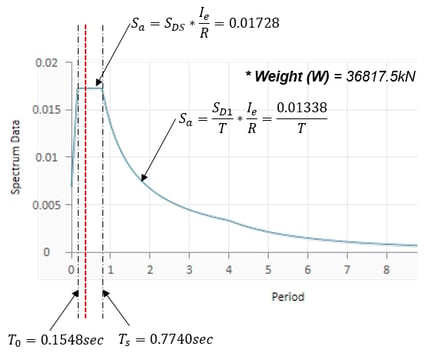
𝑇=0.35574sec
So, Sa = SDS*Ie/R = 0.01728
(red dotted line)
⇓
V= W * Sa * Mass(%)
= 36817.5 * 0.01728 * 0.7089
= 451.01kN (just for 1st mode)
 Banner Title Products
Banner Title Products






